Squamous Cell Carcinoma (SCC)
Squamous cell carcinoma is the second, most common cancer arising from
keratinocytes, in the outer layer of the skin or mucosal surfaces or from
actinic keratosis lesions.
As with AK, squamous cell carcinomas typically occur on sun-exposed areas,
and are most commonly found on the head, neck, or hands of elderly patients.
SCC can occur on the lips, inside the mouth, on the genitalia, or anywhere
on the body. SCC is invasive in nature, left untreated can spreads to
the lymph nodes, peripheral nerves and other vital structures.
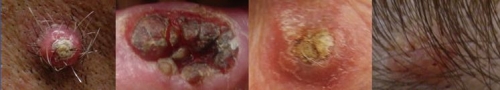
Frequent Signs and Symptoms: SCC usually looks like a small shallow ulcer with elevated margins or raised crusty, bump on the skin that eventually ulcerates
Early SCC may have the appearance of a hypertrophic actinic keratosis, might also resemble a warty lesion.
Treatment: Early detection and treatment is important to prevent complications.
Surgical excision with clear margins and Mohs micrographic surgery are
the primary methods of treatment
Diagnosis of suspicious lesion is done by punch biopsy, shave biopsy or surgical excision. Collected tissue is then examined by dermatopathologist who further provides detail report and diagnosis description. Depending upon pathology results, additional excision with skin margins or referral to might be needed.
Do wait, if you have questions or concerns about a suspicious mole or dark
spot on your skin,
schedule an appointment for a skin exam with Dr Jozef Tryzno
Call: (847) 518-9999
For those in need of reliable and comprehensive information, news and updates about specific disease, we strongly recommended to register for free account with Medscape.com, site many medical professionals use for their references.